| [1] Yang CH, Ting WJ, Day CH, et al. SHSST cyclodextrin complex prevents the fibrosis effect on CCl?-induced cirrhotic cardiomyopathy in rats through TGF-β pathway inhibition effects. Int J Mol Sci. 2014;15(5):8037-8048.
[2] Kandasamy M, Lehner B, Kraus S, et al. TGF-beta signalling in the adult neurogenic niche promotes stem cell quiescence as well as generation of new neurons. J Cell Mol Med. 2014; 18(7):1444-1459.
[3] Han X, Yang N, Cui Y, et al. Simvastatin mobilizes bone marrow stromal cells migrating to injured areas and promotes functional recovery after spinal cord injury in the rat. Neurosci Lett. 2012;521(2):136-141.
[4] Mironov SL, Skorova E, Hartelt N, et al. Remodelling of the respiratory network in a mouse model of Rett syndrome depends on brain-derived neurotrophic factor regulated slow calcium buffering. J Physiol. 2009;587(Pt 11):2473-2485.
[5] Wang BG, Zhu QS, Man XX, et al. Ginsenoside Rd inhibits apoptosis following spinal cord ischemia/reperfusion injury. Neural Regen Res. 2014;9(18):1678-1687.
[6] 方欣,周朋,闫旭升,等.人参皂苷Rg1促进大鼠坐骨神经损伤后再生的作用[J].解剖学杂志,2013,36(1):70-73.
[7] Esmaeili M, Berry M, Logan A, et al. Decorin treatment of spinal cord injury. Neural Regen Res. 2014;9(18):1653-1656.
[8] Haenzi S, Stefanics G, Lanaras T, et al. Altered cortical activation from the hand after facial botulinum toxin treatment. Ann Clin Transl Neurol. 2014;1(1):64-68.
[9] Aloe L, Bianchi P, De Bellis A, et al. Intranasal nerve growth factor bypasses the blood-brain barrier and affects spinal cord neurons in spinal cord injury. Neural Regen Res. 2014;9(10): 1025-1030.
[10] David S, Zarruk JG, Ghasemlou N. Inflammatory pathways in spinal cord injury. Int Rev Neurobiol. 2012;106:127-152.
[11] Song F, Tian M, Zhang H. Molecular imaging in stem cell therapy for spinal cord injury. Biomed Res Int. 2014;2014: 759514.
[12] 崔学文,刘自文,田纪伟.脊髓损伤后髓鞘相关抑制因子的作用机制及基因治疗现状[J].中国矫形外科杂志,2012(2):141-143.
[13] 李念龙,于占革.骨髓间充质干细胞移植治疗脊髓损伤的研究进展[J].中国矫形外科杂志,2012,20(4):343-345.
[14] Wada T, Honda M, Minami I, et al. Highly efficient differentiation and enrichment of spinal motor neurons derived from human and monkey embryonic stem cells. PLoS One. 2009;4(8):e6722.
[15] Oliveri RS, Bello S, Biering-Sørensen F. Mesenchymal stem cells improve locomotor recovery in traumatic spinal cord injury: systematic review with meta-analyses of rat models. Neurobiol Dis. 2014;62:338-353.
[16] Parry PV, Engh JA. Promotion of neuronal recovery following experimental SCI via direct inhibition of glial scar formation. Neurosurgery. 2012;70(6):N10-11.
[17] Yang R, Guo L2, Wang P1, et al. Epidemiology of spinal cord injuries and risk factors for complete injuries in Guangdong, China: a retrospective study. PLoS One. 2014;9(1):e84733.
[18] Jaerve A, Schiwy N, Schmitz C, et al. Differential effect of aging on axon sprouting and regenerative growth in spinal cord injury. Exp Neurol. 2011;231(2):284-294.
[19] 刘小康,徐建广,连小峰,等.大鼠钳夹式急性脊髓损伤模型的制备与评价[J].中国矫形外科杂志,2012,20(14):1318-1322.
[20] Binan L, Ajji A, De Crescenzo G, et al. Approaches for neural tissue regeneration. Stem Cell Rev. 2014;10(1):44-59.
[21] Saha N, Kolev MV, Semavina M, et al. Ganglioside mediate the interaction between Nogo receptor 1 and LINGO-1. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2011;413(1):92-97.
[22] Gagnon DH, Babineau AC, Champagne A, et al. Pushrim biomechanical changes with progressive increases in slope during motorized treadmill manual wheelchair propulsion in individuals with spinal cord injury. J Rehabil Res Dev. 2014; 51(5):789-802.
[23] O'Brien CF. Treatment of spasticity with botulinum toxin. Clin J Pain. 2002;18(6 Suppl):S182-190.
[24] Molazem Z, Falahati T, Jahanbin I, et al. The effect of psycho-educational interventions on the quality of life of the family caregivers of the patients with spinal cord injury: a randomized controlled trial. Int J Community Based Nurs Midwifery. 2014;2(1):31-39. |
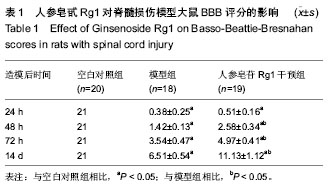
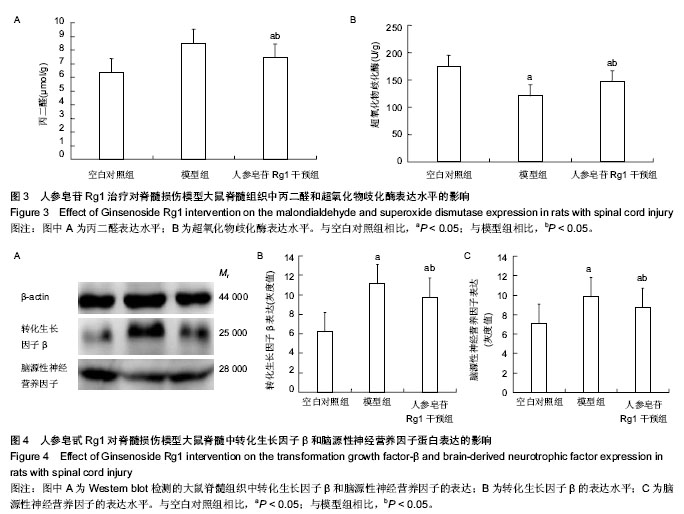
.jpg)